Overview: HEPES Buffered Saline (HBS)
Overview
HEPES is a zwitterionic buffering compound, falling under the category of Good’s buffers due to its buffering properties and solubility. HEPES buffered saline (HBS) is a formulation optimized for maintaining isotonicity and pH stability under physiological conditions.
HEPES Buffered Saline (HBS)
Composition of HEPES Buffered Saline:
- HEPES: Acts as the buffer to maintain pH, especially in the range of 6.8 to 8.2.
- NaCl (Sodium Chloride): Provides osmotic balance.
- pH Range: Adjusted to physiological pH of 7.2–7.6 using NaOH or HCl, suitable for physiological experiments.
Features:
- High buffering capacity.
- Better pH stability compared to bicarbonate buffers, especially in open systems without CO₂.
- Non-toxic to cells.
Applications:
- Cell Culture: Maintains a stable pH in environments not controlled by CO₂.
- Protein Biochemistry: Suitable for protein stability and activity assays.
- Immunological Assays: Used in ELISA or flow cytometry.
- Transfection Protocols: Facilitates the introduction of genetic material into cells.
HBS-EP and HBS-EP+ (HEPES Buffered Saline with EDTA and Tween 20)
Composition of HBS-EP and HBS-EP+:
- HEPES: Acts as the primary buffer, maintaining pH stability (typically around pH 7.4).
- NaCl (Sodium Chloride): Maintains ionic strength and isotonicity.
- EDTA (Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid): A chelating agent that binds divalent cations like Mg²⁺ and Ca²⁺ to prevent unwanted aggregation or nonspecific interactions.
- Tween 20: A non-ionic surfactant that minimizes non-specific binding to sensor surfaces or other proteins.
Features:
- Reduces non-specific protein binding to surfaces.
- Stabilizes biomolecules by preventing aggregation.
Applications:
- Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR): Widely used as a running buffer in SPR for studying biomolecular interactions.
- Protein-Ligand Binding: Improves signal clarity by reducing background noise.
- Antibody-Antigen Studies: Prevents aggregation and enhances interaction specificity.
HEPES-EP and HEPES EP+ buffers in SPR Workflows
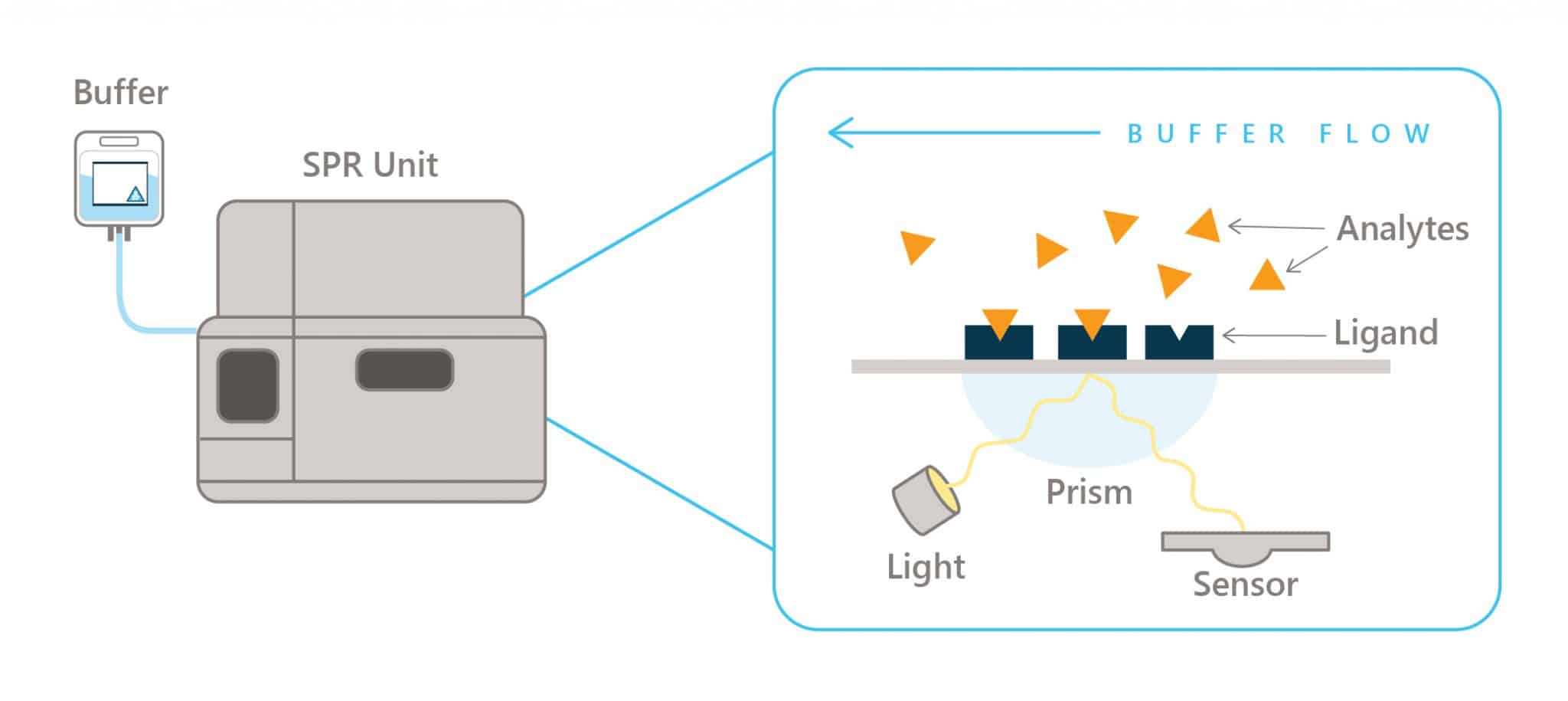
HEPES buffered saline is a key reagent for multiple steps in SPR analysis. SPR, an acronym for surface plasmon resonance, is an analysis technique for assessing binding characteristics and related biochemical dynamics between molecules (1,2). HEPES buffered saline is used to prime SPR in-unit pumps. HEPES-buffered saline formulations are tailored to specific experimental needs, serving as both a running buffer and a binding buffer in SPR workflow. These formulations contain identical concentrations of HEPES and sodium chloride but incorporate polysorbate P20 (also known as Tween-20) as a detergent and/or EDTA as a chelating agent. Tween-20 is often used at 0.005% (v/v) concentrations in HEPES EP buffers while at 0.05% concentrations in EP+ buffers. Other HBS buffers used are: HBS-N and HBS-N+ Buffers (HEPES and NaCl solution).
HEPES and HEPES Buffered Saline at Boston BioProducts
Boston BioProducts offers several different formulations of HEPES buffered saline for research use and further manufacturing. Explore our Catalog Offerings best fit for your needs, or Custom Manufacturing options.
Build a Custom Reagent Quickly
References:
-
- Schuck, P. (1997). Use of surface plasmon resonance to probe the equilibrium and dynamic aspects of interactions between biological macromolecules. Annual Review of Biophysics. 26, 541-566.
- Drescher, D. G., Ramakrishnan, N. A. and Drescher, M. J. (2009). Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) analysis of binding interactions of proteins in inner-ear sensory epithelia. Methods in molecular biology. 493, 323–343.
